Using Secret management service via Vault's GUI and client
Although using Secret management service via FedCloud client is strongly recommended, the service is fully compatible with Hashicorp’s Vault and can be used via the web-based GUI or Vault's native client tool and libraries. The native client tool is more complicated but it has some functionalities not offered by FedCloud client, e.g. token renew. The compatibility also enable integration of existing services and applications that are already using Vault, to the Secret management service.
Using Secret management service via web-based GUI
Open https://vault.services.fedcloud.eu:8200 in your browser.
Choose OIDC authentication method in the pulldown menu, and click on the button
Sign in with OIDC provider
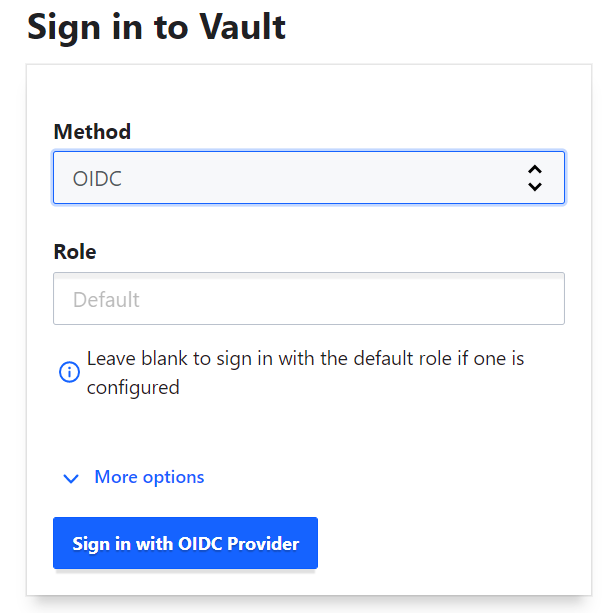
Login via EGI Check-in and authorize the Vault GUI.
You have logged into the Vault GUI. Each user has a private secret space, a "home directory" in the secret engine
secrets, with EGI Check-in ID as the folder name.
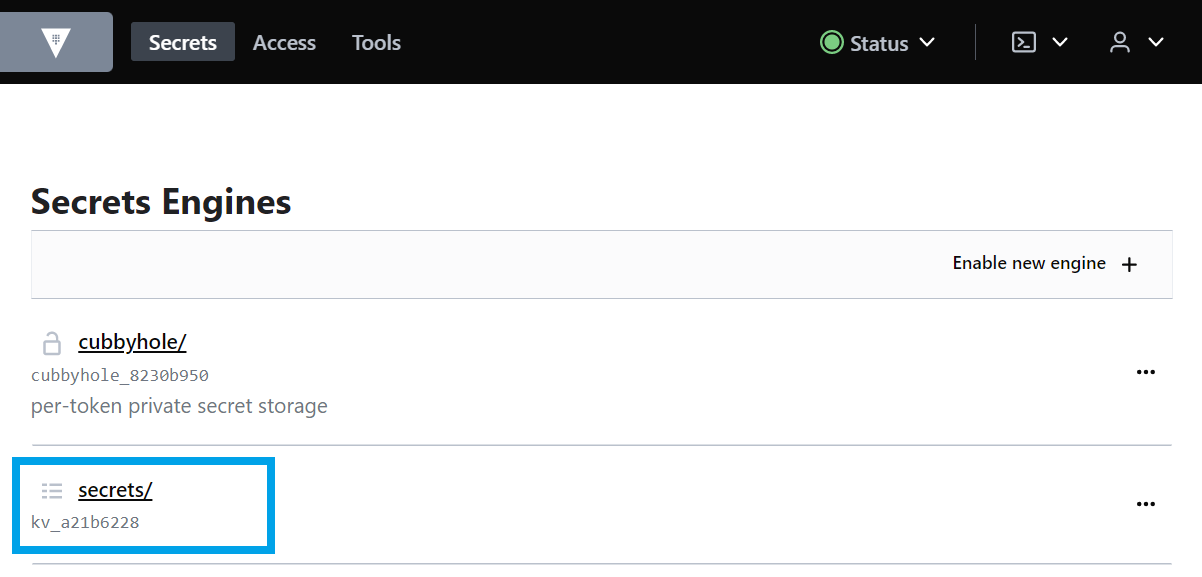
The "home directory" is not created automatically, so for the first time login, you may have to create it. In the
secretsfolder, click onCreate secreton the right side of your screen and create a new secret with a path starting with your EGI Check-in ID (e0b6.…@egi.euin the screenshot)
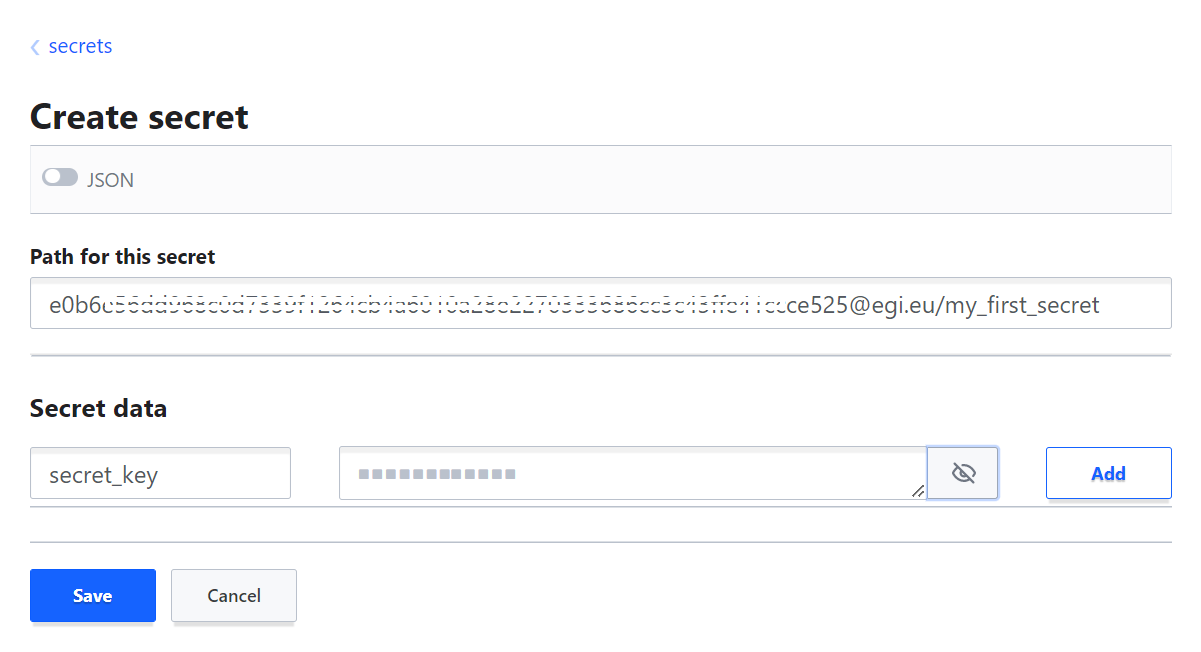
Your "home directory" will be created together with your first secret. Click on
secretsfolder, then your ID in the EGI Check-in to enter your private secret space, then browse/view/edit your secrets
Using Secret management service via Vault CLI and access token
Install Vault CLI if needed. See https://www.vaultproject.io/downloads for downloading Vault for different OS.
Set environment for URL of Vault server:
$ export VAULT_ADDR=https://vault.services.fedcloud.eu:8200
Get your EGI Check-in access token (e.g. from EGI Check-in Token Portal or oidc-agent) and set it to an environment variable:
$ export ACCESS_TOKEN="ADD_YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN_HERE"
Login to Vault using access tokens:
$ vault write auth/jwt/login jwt=$ACCESS_TOKEN
Key Value
--- -----
token s.XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
The command will return a Vault’s token in the form
token s.XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX. Save the token to an environment variable and use it for manipulation with secrets in Vault
$ export VAULT_TOKEN="s.XXXXXXXXXXXXXX"
For convenience, set your Vault’s home path to an environment variable
$ export VAULT_HOME=/secrets/YOUR_CHECKIN_ID@egi.eu/
List secrets in your "home directory". VAULT_ADDR and VAULT_TOKEN must be set:
$ vault list $VAULT_HOME
Create a new secret with name
testin your "home directory", store valuevalue1in keykey1:
$ vault write $VAULT_HOME/test key1=value1
Read your secret:
$ vault read $VAULT_HOME/test
Key Value
--- -----
refresh_interval 768h
key1 value1
There are alternative commands kv put, kv get for write, read. The full list of Vault
commands is available at https://www.vaultproject.io/docs/commands
Using Vault via REST API or external clients
Vault has a REST API with similar inputs like the CLI. There is a long list of libraries and external clients/tools for accessing secrets in Vault. See https://www.vaultproject.io/api or https://www.vaultproject.io/api-docs/relatedtools for more details.